Coursera
Ungraded Lab: CelebA GAN Experiments
This lab will demonstrate a GAN trained on the CelebA dataset. This is a resource-intensive task so you will use a TPU and a distributed strategy to train the network. It will take 40 to 50 minutes to run the entire exercise. Afterwards, you will see a gif showing new faces generated by the trained model.
Imports
# install tensorflow_addons
!pip install -U tensorflow-addons
Collecting tensorflow-addons
Downloading tensorflow_addons-0.21.0-cp310-cp310-manylinux_2_17_x86_64.manylinux2014_x86_64.whl (612 kB)
[2K [90m━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━[0m [32m612.1/612.1 kB[0m [31m9.2 MB/s[0m eta [36m0:00:00[0m
[?25hRequirement already satisfied: packaging in /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages (from tensorflow-addons) (23.2)
Collecting typeguard<3.0.0,>=2.7 (from tensorflow-addons)
Downloading typeguard-2.13.3-py3-none-any.whl (17 kB)
Installing collected packages: typeguard, tensorflow-addons
Successfully installed tensorflow-addons-0.21.0 typeguard-2.13.3
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow_datasets as tfds
from tensorflow.keras.utils import plot_model
from tensorflow.keras import layers
import tensorflow_addons as tfa
import os
import zipfile
import glob
import urllib.request
from enum import Enum
from tqdm import tqdm
from functools import partial
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
from IPython.display import display
from IPython.display import Image as IpyImage
import imageio
import cv2
/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/tensorflow_addons/utils/tfa_eol_msg.py:23: UserWarning:
TensorFlow Addons (TFA) has ended development and introduction of new features.
TFA has entered a minimal maintenance and release mode until a planned end of life in May 2024.
Please modify downstream libraries to take dependencies from other repositories in our TensorFlow community (e.g. Keras, Keras-CV, and Keras-NLP).
For more information see: https://github.com/tensorflow/addons/issues/2807
warnings.warn(
Setup TPU
You will use a TPU and its corresponding distribution strategy to speed up the training. We’ve provided the setup code and helper functions below. You might recognize some of these from taking Course 2 of this Specialization.
tpu_grpc_url = "grpc://" + os.environ["COLAB_TPU_ADDR"]
tpu_cluster_resolver = tf.distribute.cluster_resolver.TPUClusterResolver(tpu_grpc_url)
tf.config.experimental_connect_to_cluster(tpu_cluster_resolver)
tf.tpu.experimental.initialize_tpu_system(tpu_cluster_resolver)
strategy = tf.distribute.experimental.TPUStrategy(tpu_cluster_resolver)
WARNING:absl:`tf.distribute.experimental.TPUStrategy` is deprecated, please use the non experimental symbol `tf.distribute.TPUStrategy` instead.
class Reduction(Enum):
NONE = 0
SUM = 1
MEAN = 2
CONCAT = 3
def distributed(*reduction_flags):
def _decorator(fun):
def per_replica_reduction(z, flag):
if flag == Reduction.NONE:
return z
elif flag == Reduction.SUM:
return strategy.reduce(tf.distribute.ReduceOp.SUM, z, axis=None)
elif flag == Reduction.MEAN:
return strategy.reduce(tf.distribute.ReduceOp.MEAN, z, axis=None)
elif flag == Reduction.CONCAT:
z_list = strategy.experimental_local_results(z)
return tf.concat(z_list, axis=0)
else:
raise NotImplementedError()
@tf.function
def _decorated_fun(*args, **kwargs):
fun_result = strategy.run(fun, args=args, kwargs=kwargs)
if len(reduction_flags) == 0:
assert fun_result is None
return
elif len(reduction_flags) == 1:
assert type(fun_result) is not tuple and fun_redult is not None
return per_replica_reduction(fun_result, *reduction_flags)
else:
assert type(fun_result) is tuple
return tuple((per_replica_reduction(fr, rf) for fr, rf in zip(fun_result, reduction_flags)))
return _decorated_fun
return _decorator
Download and Prepare the Dataset
Next, you will fetch the celebrity faces dataset. We’ve hosted a copy of the data in a Google Drive but the filesize is around 1GB so it will take some time to download.
# make a data directory
try:
os.mkdir('/tmp/celeb')
except OSError:
pass
# download the dataset archive
data_url = "https://storage.googleapis.com/learning-datasets/Resources/archive.zip"
data_file_name = "archive.zip"
download_dir = '/tmp/celeb/'
urllib.request.urlretrieve(data_url, data_file_name)
# extract the zipped file
zip_ref = zipfile.ZipFile(data_file_name, 'r')
zip_ref.extractall(download_dir)
zip_ref.close()
You will then prepare the dataset. Preprocessing steps include cropping and transforming the pixel values to the range [-1, 1]. Training batches are then prepared so it can be fed into the model later.
def load_celeba(batch_size, resize=64, crop_size=128):
"""Creates batches of preprocessed images from the JPG files
Args:
batch_size - batch size
resize - size in pixels to resize the images
crop_size - size to crop from the image
Returns:
prepared dataset
"""
# initialize zero-filled array equal to the size of the dataset
image_paths = sorted(glob.glob("/tmp/celeb/img_align_celeba/img_align_celeba/*.jpg"))
images = np.zeros((len(image_paths), resize, resize, 3), np.uint8)
print("Creating Images")
# crop and resize the raw images then put into the array
for i, path in tqdm(enumerate(image_paths)):
with Image.open(path) as img:
left = (img.size[0] - crop_size) // 2
top = (img.size[1] - crop_size) // 2
right = left + crop_size
bottom = top + crop_size
img = img.crop((left, top, right, bottom))
img = img.resize((resize, resize), Image.LANCZOS)
images[i] = np.asarray(img, np.uint8)
# split the images array into two
split_n = images.shape[0] // 2
images1, images2 = images[:split_n], images[split_n:2 * split_n]
del images
# preprocessing function to convert the pixel values into the range [-1,1]
def preprocess(img):
x = tf.cast(img, tf.float32) / 127.5 - 1.0
return x
# use the preprocessing function on the arrays and create batches
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((images1, images2))
dataset = dataset.map(
lambda x1, x2: (preprocess(x1), preprocess(x2))
).shuffle(4096).batch(batch_size, drop_remainder=True).prefetch(tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE)
return dataset
# use the function above to load and prepare the dataset
batch_size = 8
batch_size = batch_size * strategy.num_replicas_in_sync
dataset = load_celeba(batch_size)
out_dir = "celeba_out"
Creating Images
202599it [04:34, 738.35it/s]
Build the Model
Next, you will build the generator and discriminator. As mentioned in the lecture, the code in this notebook is generalized to make it easy to reconfigure (such as choosing the type of normalization). With that, you will notice a lot of extra code, mostly related to gradient penalty. You can ignore those and we’ve set the defaults to the reflect the architecture shown in class.
You can try the other settings once you’ve gone through these defaults. Additional modes made available are based on DRAGAN and WGAN-GP and you can read about it here and here. These settings are reconfigured using the utilities below.
# Utilities
def _get_norm_layer(norm):
if norm == 'NA':
return lambda: lambda x: x
elif norm == 'batch_normalization':
return layers.BatchNormalization
elif norm == 'instance_normalization':
return tfa.layers.InstanceNormalization
elif norm == 'layer_normalization':
return layers.LayerNormalization
def get_initializers():
return (tf.keras.initializers.RandomNormal(mean=0.0, stddev=0.02), # conv initializer
tf.keras.initializers.RandomNormal(mean=1.0, stddev=0.02)) # bn gamma initializer
def gradient_penalty(f, real, fake, mode):
def _gradient_penalty(f, real, fake=None):
def _interpolate(a, b=None):
if b is None: # interpolation in DRAGAN
beta = tf.random.uniform(shape=tf.shape(a), minval=0., maxval=1.)
b = a + 0.5 * tf.math.reduce_std(a) * beta
shape = [tf.shape(a)[0]] + [1] * (a.shape.ndims - 1)
alpha = tf.random.uniform(shape=shape, minval=0., maxval=1.)
inter = a + alpha * (b - a)
inter.set_shape(a.shape)
return inter
x = _interpolate(real, fake)
with tf.GradientTape() as t:
t.watch(x)
pred = f(x)
grad = t.gradient(pred, x)
norm = tf.norm(tf.reshape(grad, [tf.shape(grad)[0], -1]), axis=1)
gp = tf.reduce_mean((norm - 1.)**2)
return gp
if mode == 'none':
gp = tf.constant(0, dtype=real.dtype)
elif mode == 'dragan':
gp = _gradient_penalty(f, real)
elif mode == 'wgan-gp':
gp = _gradient_penalty(f, real, fake)
return gp
Generator
You will first define the generator layers. Again, you will notice some extra code but the default will follow the architecture in class. Like the DCGAN you previously built, the model here primarily uses blocks containing Conv2D, BatchNormalization, and ReLU layers.
def create_generator(input_shape=(1, 1, 128),
output_channels=3,
dim=64,
n_upsamplings=4,
norm='batch_normalization',
name='generator'):
Normalization = _get_norm_layer(norm)
conv_initializer, bn_gamma_initializer = get_initializers()
# 0
x = inputs = tf.keras.Input(shape=input_shape)
# 1: 1x1 -> 4x4
dimensions = min(dim * 2 ** (n_upsamplings - 1), dim * 8)
x = layers.Conv2DTranspose(
dimensions, 4, strides=1, padding='valid', use_bias=False,
# kernel_initializer=conv_initializer
)(x)
x = Normalization(
# gamma_initializer=bn_gamma_initializer
)(x)
x = layers.ReLU()(x)
# 2: upsamplings, 4x4 -> 8x8 -> 16x16 -> ...
for i in range(n_upsamplings - 1):
dimensions = min(dim * 2 ** (n_upsamplings - 2 - i), dim * 8)
x = layers.Conv2DTranspose(
dimensions, 4, strides=2, padding='same', use_bias=False,
# kernel_initializer=conv_initializer
)(x)
x = Normalization(
# gamma_initializer=bn_gamma_initializer
)(x)
x = layers.ReLU()(x)
x = layers.Conv2DTranspose(
output_channels, 4, strides=2, padding='same',
# kernel_initializer=conv_initializer
)(x)
outputs = layers.Activation('tanh')(x)
return tf.keras.Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs, name=name)
Discriminator
The discriminator will use strided convolutions to reduce the dimensionality of the features. These will be connected to a LeakyReLU activation.
def create_discriminator(input_shape=(64, 64, 3),
dim=64,
n_downsamplings=4,
norm='batch_normalization',
name='discriminator'):
Normalization = _get_norm_layer(norm)
conv_initializer, bn_gamma_initializer = get_initializers()
# 0
x = inputs = tf.keras.Input(shape=input_shape)
# 1: downsamplings, ... -> 16x16 -> 8x8 -> 4x4
x = layers.Conv2D(dim, 4, strides=2, padding='same',
# kernel_initializer=conv_initializer
)(x)
x = layers.LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(x)
for i in range(n_downsamplings - 1):
dimensions = min(dim * 2 ** (i + 1), dim * 8)
x = layers.Conv2D(dimensions, 4, strides=2, padding='same', use_bias=False,
# kernel_initializer=conv_initializer
)(x)
x = Normalization(
# gamma_initializer=bn_gamma_initializer
)(x)
x = layers.LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(x)
# 2: logit
outputs = layers.Conv2D(1, 4, strides=1, padding='valid',
# kernel_initializer=conv_initializer
)(x)
return tf.keras.Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs, name=name)
With the layers for the generator and discriminator defined, you can now create the models and set it up for training.
# Settings
resize = 64
shape = (resize, resize, 3)
z_dim = 128
n_G_upsamplings = n_D_downsamplings = 4
gradient_penalty_mode = 'none'
if gradient_penalty_mode == 'none':
d_norm = 'batch_normalization'
elif gradient_penalty_mode in ['dragan', 'wgan-gp']:
# Avoid using BN with GP
d_norm = 'layer_normalization'
gradient_penalty_weight = 10.0
# Build the GAN
with strategy.scope():
# create the generator model
model_G = create_generator(input_shape=(1, 1, z_dim), output_channels=shape[-1], n_upsamplings=n_G_upsamplings)
# create the discriminator model
model_D = create_discriminator(input_shape=shape, n_downsamplings=n_D_downsamplings, norm=d_norm)
# print summaries
model_G.summary()
model_D.summary()
# set optimizers
param_G = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(lr=0.0002, beta_1=0.5)
param_D = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(lr=0.0002, beta_1=0.5)
# create distributed dataset
dataset = strategy.experimental_distribute_dataset(dataset)
# set the loss function
loss_func = tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(
from_logits=True,
reduction=tf.keras.losses.Reduction.NONE
)
Model: "generator"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
input_1 (InputLayer) [(None, 1, 1, 128)] 0
conv2d_transpose (Conv2DTra (None, 4, 4, 512) 1048576
nspose)
batch_normalization (BatchN (None, 4, 4, 512) 2048
ormalization)
re_lu (ReLU) (None, 4, 4, 512) 0
conv2d_transpose_1 (Conv2DT (None, 8, 8, 256) 2097152
ranspose)
batch_normalization_1 (Batc (None, 8, 8, 256) 1024
hNormalization)
re_lu_1 (ReLU) (None, 8, 8, 256) 0
conv2d_transpose_2 (Conv2DT (None, 16, 16, 128) 524288
ranspose)
batch_normalization_2 (Batc (None, 16, 16, 128) 512
hNormalization)
re_lu_2 (ReLU) (None, 16, 16, 128) 0
conv2d_transpose_3 (Conv2DT (None, 32, 32, 64) 131072
ranspose)
batch_normalization_3 (Batc (None, 32, 32, 64) 256
hNormalization)
re_lu_3 (ReLU) (None, 32, 32, 64) 0
conv2d_transpose_4 (Conv2DT (None, 64, 64, 3) 3075
ranspose)
activation (Activation) (None, 64, 64, 3) 0
=================================================================
Total params: 3,808,003
Trainable params: 3,806,083
Non-trainable params: 1,920
_________________________________________________________________
Model: "discriminator"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
input_2 (InputLayer) [(None, 64, 64, 3)] 0
conv2d (Conv2D) (None, 32, 32, 64) 3136
leaky_re_lu (LeakyReLU) (None, 32, 32, 64) 0
conv2d_1 (Conv2D) (None, 16, 16, 128) 131072
batch_normalization_4 (Batc (None, 16, 16, 128) 512
hNormalization)
leaky_re_lu_1 (LeakyReLU) (None, 16, 16, 128) 0
conv2d_2 (Conv2D) (None, 8, 8, 256) 524288
batch_normalization_5 (Batc (None, 8, 8, 256) 1024
hNormalization)
leaky_re_lu_2 (LeakyReLU) (None, 8, 8, 256) 0
conv2d_3 (Conv2D) (None, 4, 4, 512) 2097152
batch_normalization_6 (Batc (None, 4, 4, 512) 2048
hNormalization)
leaky_re_lu_3 (LeakyReLU) (None, 4, 4, 512) 0
conv2d_4 (Conv2D) (None, 1, 1, 1) 8193
=================================================================
Total params: 2,767,425
Trainable params: 2,765,633
Non-trainable params: 1,792
_________________________________________________________________
WARNING:absl:`lr` is deprecated in Keras optimizer, please use `learning_rate` or use the legacy optimizer, e.g.,tf.keras.optimizers.legacy.Adam.
WARNING:absl:`lr` is deprecated in Keras optimizer, please use `learning_rate` or use the legacy optimizer, e.g.,tf.keras.optimizers.legacy.Adam.
Training
Finally, you can now train the model. We’ve provided some helper functions for visualizing and saving the images per epoch.
# Utilities
def make_grid(imgs, nrow, padding=0):
assert imgs.ndim == 4 and nrow > 0
batch, height, width, ch = imgs.shape
n = nrow * (batch // nrow + np.sign(batch % nrow))
ncol = n // nrow
pad = np.zeros((n - batch, height, width, ch), imgs.dtype)
x = np.concatenate([imgs, pad], axis=0)
# border padding if required
if padding > 0:
x = np.pad(x, ((0, 0), (0, padding), (0, padding), (0, 0)),
"constant", constant_values=(0, 0))
height += padding
width += padding
x = x.reshape(ncol, nrow, height, width, ch)
x = x.transpose([0, 2, 1, 3, 4]) # (ncol, height, nrow, width, ch)
x = x.reshape(height * ncol, width * nrow, ch)
if padding > 0:
x = x[:(height * ncol - padding),:(width * nrow - padding),:]
return x
def save_img(imgs, filepath, nrow, padding=0):
grid_img = make_grid(imgs, nrow, padding=padding)
grid_img = ((grid_img + 1.0) * 127.5).astype(np.uint8)
with Image.fromarray(grid_img) as img:
img.save(filepath)
This function defines the training on a given batch. It does the two-phase training discussed in class.
- First, you train the discriminator to distinguish between fake and real images.
- Next, you train the generator to create fake images that will fool the discriminator.
@distributed(Reduction.SUM, Reduction.SUM, Reduction.CONCAT)
def train_on_batch(real_img1, real_img2):
'''trains the GAN on a given batch'''
# concatenate the real image inputs
real_img = tf.concat([real_img1, real_img2], axis=0)
# PHASE ONE - train the discriminator
with tf.GradientTape() as d_tape:
# create noise input
z = tf.random.normal(shape=(real_img.shape[0], 1, 1, z_dim))
# generate fake images
fake_img = model_G(z)
# feed the fake images to the discriminator
fake_out = model_D(fake_img)
# feed the real images to the discriminator
real_out = model_D(real_img)
# use the loss function to measure how well the discriminator
# labels fake or real images
d_fake_loss = loss_func(tf.zeros_like(fake_out), fake_out)
d_real_loss = loss_func(tf.ones_like(real_out), real_out)
# get the total loss
d_loss = (d_fake_loss + d_real_loss)
d_loss = tf.reduce_sum(d_loss) / (batch_size * 2)
# Gradient Penalty (ignore if you set mode to `none`)
gp = gradient_penalty(partial(model_D, training=True), real_img, fake_img, mode=gradient_penalty_mode)
gp = gp / (batch_size * 2)
d_loss = d_loss + gp * gradient_penalty_weight
# get the gradients
gradients = d_tape.gradient(d_loss, model_D.trainable_variables)
# update the weights of the discriminator
param_D.apply_gradients(zip(gradients, model_D.trainable_variables))
# PHASE TWO - train the generator
with tf.GradientTape() as g_tape:
# create noise input
z = tf.random.normal(shape=(real_img.shape[0], 1, 1, z_dim))
# generate fake images
fake_img = model_G(z)
# feed fake images to the discriminator
fake_out = model_D(fake_img)
# use loss function to measure how well the generator
# is able to trick the discriminator (i.e. model_D should output 1's)
g_loss = loss_func(tf.ones_like(fake_out), fake_out)
g_loss = tf.reduce_sum(g_loss) / (batch_size * 2)
# get the gradients
gradients = g_tape.gradient(g_loss, model_G.trainable_variables)
# update the weights of the generator
param_G.apply_gradients(zip(gradients, model_G.trainable_variables))
# return the losses and fake images for monitoring
return d_loss, g_loss, fake_img
This will start the training loop. We set the number of epochs but feel free to revise it. From initial runs, it takes around 50 seconds to complete 1 epoch. We’ve setup a progress bar to display the losses per epoch and there is code as well to print the fake images generated.
# generate a batch of noisy input
test_z = tf.random.normal(shape=(64, 1, 1, z_dim))
# start loop
for epoch in range(30):
with tqdm(dataset) as pbar:
pbar.set_description(f"[Epoch {epoch}]")
for step, (X1, X2) in enumerate(pbar):
# train on the current batch
d_loss, g_loss, fake = train_on_batch(X1, X2)
# display the losses
pbar.set_postfix({"g_loss": g_loss.numpy(), "d_loss": d_loss.numpy()})
# generate fake images
fake_img = model_G(test_z)
# save output
if not os.path.exists(out_dir):
os.makedirs(out_dir)
file_path = out_dir+f"/epoch_{epoch:04}.png"
save_img(fake_img.numpy()[:64], file_path, 8)
# display gallery of fake faces
if epoch % 1 == 0:
with Image.open(file_path) as img:
plt.imshow(np.asarray(img))
plt.show()
[Epoch 0]: : 1582it [01:05, 30.72it/s, g_loss=97.5, d_loss=21.3]Exception ignored in: <function Executor.__del__ at 0x7fe65c0c0940>
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/tensorflow/python/eager/executor.py", line 46, in __del__
self.wait()
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/tensorflow/python/eager/executor.py", line 65, in wait
pywrap_tfe.TFE_ExecutorWaitForAllPendingNodes(self._handle)
tensorflow.python.framework.errors_impl.OutOfRangeError: End of sequence
[Epoch 0]: : 1582it [01:05, 24.26it/s, g_loss=97.5, d_loss=21.3]
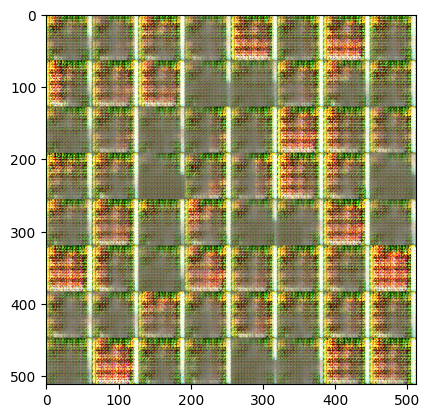
[Epoch 1]: : 1581it [00:54, 13.63it/s, g_loss=0.361, d_loss=2.91] Exception ignored in: <function Executor.__del__ at 0x7fe65c0c0940>
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/tensorflow/python/eager/executor.py", line 46, in __del__
self.wait()
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/tensorflow/python/eager/executor.py", line 65, in wait
pywrap_tfe.TFE_ExecutorWaitForAllPendingNodes(self._handle)
tensorflow.python.framework.errors_impl.OutOfRangeError: End of sequence
[Epoch 1]: : 1582it [00:54, 29.17it/s, g_loss=0.361, d_loss=2.91]
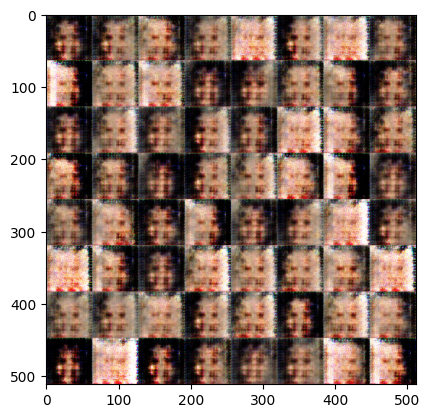
[Epoch 2]: : 1581it [00:55, 28.97it/s, g_loss=0.000791, d_loss=5.52]Exception ignored in: <function Executor.__del__ at 0x7fe65c0c0940>
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/tensorflow/python/eager/executor.py", line 46, in __del__
self.wait()
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/tensorflow/python/eager/executor.py", line 65, in wait
pywrap_tfe.TFE_ExecutorWaitForAllPendingNodes(self._handle)
tensorflow.python.framework.errors_impl.OutOfRangeError: End of sequence
[Epoch 2]: : 1582it [00:55, 28.61it/s, g_loss=0.000791, d_loss=5.52]
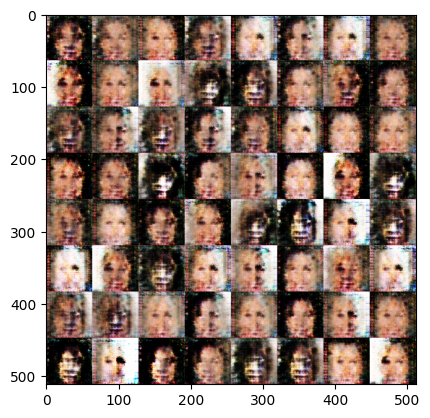
[Epoch 3]: : 1579it [00:50, 34.37it/s, g_loss=2.4e-5, d_loss=1.35]Exception ignored in: <function Executor.__del__ at 0x7fe65c0c0940>
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/tensorflow/python/eager/executor.py", line 46, in __del__
self.wait()
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/tensorflow/python/eager/executor.py", line 65, in wait
pywrap_tfe.TFE_ExecutorWaitForAllPendingNodes(self._handle)
tensorflow.python.framework.errors_impl.OutOfRangeError: End of sequence
[Epoch 3]: : 1582it [00:50, 31.42it/s, g_loss=2.4e-5, d_loss=1.35]
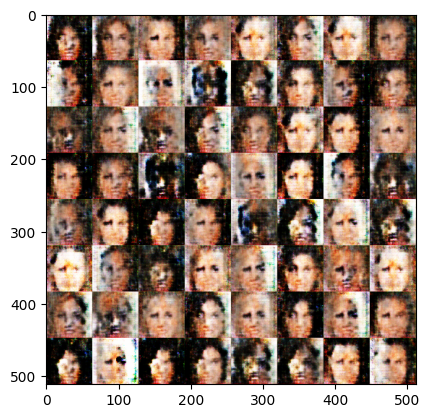
[Epoch 4]: : 1579it [00:58, 32.76it/s, g_loss=0.472, d_loss=0.338]Exception ignored in: <function Executor.__del__ at 0x7fe65c0c0940>
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/tensorflow/python/eager/executor.py", line 46, in __del__
self.wait()
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/tensorflow/python/eager/executor.py", line 65, in wait
pywrap_tfe.TFE_ExecutorWaitForAllPendingNodes(self._handle)
tensorflow.python.framework.errors_impl.OutOfRangeError: End of sequence
[Epoch 4]: : 1582it [00:58, 27.01it/s, g_loss=0.472, d_loss=0.338]
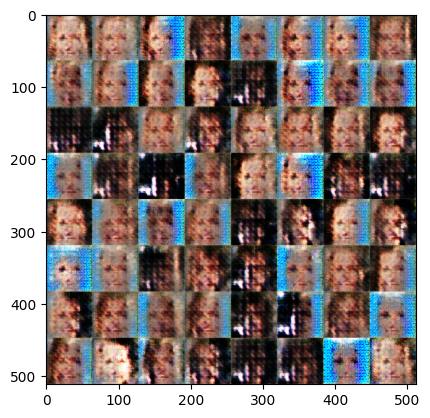
[Epoch 5]: : 1582it [00:52, 30.17it/s, g_loss=0.125, d_loss=0.234]Exception ignored in: <function Executor.__del__ at 0x7fe65c0c0940>
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/tensorflow/python/eager/executor.py", line 46, in __del__
self.wait()
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/tensorflow/python/eager/executor.py", line 65, in wait
pywrap_tfe.TFE_ExecutorWaitForAllPendingNodes(self._handle)
tensorflow.python.framework.errors_impl.OutOfRangeError: End of sequence
[Epoch 5]: : 1582it [00:52, 30.20it/s, g_loss=0.125, d_loss=0.234]
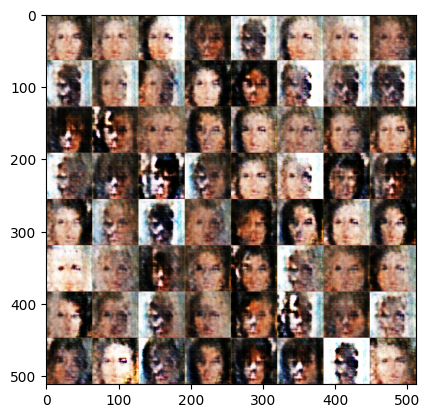
[Epoch 6]: : 1580it [00:55, 31.89it/s, g_loss=0.322, d_loss=0.423]Exception ignored in: <function Executor.__del__ at 0x7fe65c0c0940>
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/tensorflow/python/eager/executor.py", line 46, in __del__
self.wait()
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/tensorflow/python/eager/executor.py", line 65, in wait
pywrap_tfe.TFE_ExecutorWaitForAllPendingNodes(self._handle)
tensorflow.python.framework.errors_impl.OutOfRangeError: End of sequence
[Epoch 6]: : 1582it [00:55, 28.38it/s, g_loss=0.322, d_loss=0.423]
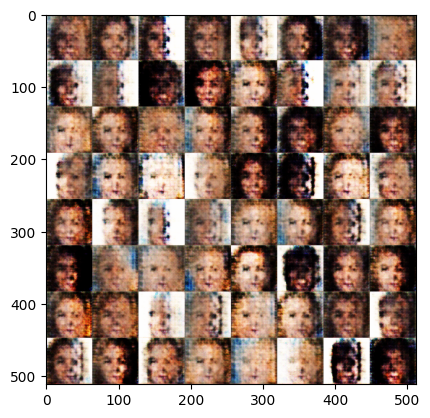
[Epoch 7]: : 1580it [00:51, 33.25it/s, g_loss=0.251, d_loss=0.402]Exception ignored in: <function Executor.__del__ at 0x7fe65c0c0940>
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/tensorflow/python/eager/executor.py", line 46, in __del__
self.wait()
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/tensorflow/python/eager/executor.py", line 65, in wait
pywrap_tfe.TFE_ExecutorWaitForAllPendingNodes(self._handle)
tensorflow.python.framework.errors_impl.OutOfRangeError: End of sequence
[Epoch 7]: : 1582it [00:51, 30.67it/s, g_loss=0.251, d_loss=0.402]
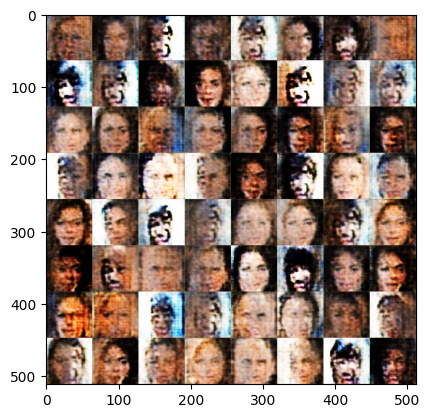
[Epoch 8]: : 1408it [00:48, 31.28it/s, g_loss=62, d_loss=26.2]
Display GIF sample results
You can run the cells below to display the galleries as an animation.
imgs = os.listdir('celeba_out')
imgs.sort()
imgs = [cv2.imread('celeba_out/' + i) for i in imgs]
imgs = [cv2.cvtColor(i, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) for i in imgs]
imageio.mimsave('anim.gif', imgs, fps=2)
path="anim.gif"
with open(path,'rb') as f:
display(IpyImage(data=f.read(), format='png'))
Congratulations on completing the final ungraded lab for this course!