Coursera
Fine-Tune BERT for Text Classification with TensorFlow
Figure 1: BERT Classification Model
In this project, you will learn how to fine-tune a BERT model for text classification using TensorFlow and TF-Hub.
The pretrained BERT model used in this project is available on TensorFlow Hub.
Learning Objectives
By the time you complete this project, you will be able to:
- Build TensorFlow Input Pipelines for Text Data with the
tf.dataAPI - Tokenize and Preprocess Text for BERT
- Fine-tune BERT for text classification with TensorFlow 2 and TF Hub
Prerequisites
In order to be successful with this project, it is assumed you are:
- Competent in the Python programming language
- Familiar with deep learning for Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Familiar with TensorFlow, and its Keras API
Contents
This project/notebook consists of several Tasks.
- Task 1: Introduction to the Project.
- Task 2: Setup your TensorFlow and Colab Runtime
- Task 3: Download and Import the Quora Insincere Questions Dataset
- Task 4: Create tf.data.Datasets for Training and Evaluation
- Task 5: Download a Pre-trained BERT Model from TensorFlow Hub
- Task 6: Tokenize and Preprocess Text for BERT
- Task 7: Wrap a Python Function into a TensorFlow op for Eager Execution
- Task 8: Create a TensorFlow Input Pipeline with
tf.data - Task 9: Add a Classification Head to the BERT
hub.KerasLayer - Task 10: Fine-Tune BERT for Text Classification
- Task 11: Evaluate the BERT Text Classification Model
Task 2: Setup your TensorFlow and Colab Runtime.
You will only be able to use the Colab Notebook after you save it to your Google Drive folder. Click on the File menu and select “Save a copy in Drive…
Check GPU Availability
Check if your Colab notebook is configured to use Graphical Processing Units (GPUs). If zero GPUs are available, check if the Colab notebook is configured to use GPUs (Menu > Runtime > Change Runtime Type).
!nvidia-smi
Wed Feb 16 05:43:12 2022
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| NVIDIA-SMI 460.32.03 Driver Version: 460.32.03 CUDA Version: 11.2 |
|-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
| GPU Name Persistence-M| Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr. ECC |
| Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap| Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. |
| | | MIG M. |
|===============================+======================+======================|
| 0 Tesla K80 Off | 00000000:00:04.0 Off | 0 |
| N/A 64C P8 32W / 149W | 0MiB / 11441MiB | 0% Default |
| | | N/A |
+-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Processes: |
| GPU GI CI PID Type Process name GPU Memory |
| ID ID Usage |
|=============================================================================|
| No running processes found |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Install TensorFlow and TensorFlow Model Garden
import tensorflow as tf
print(tf.version.VERSION)
2.3.0
!pip install -q tensorflow==2.3.0
[31mERROR: pip's dependency resolver does not currently take into account all the packages that are installed. This behaviour is the source of the following dependency conflicts.
tables 3.7.0 requires numpy>=1.19.0, but you have numpy 1.18.5 which is incompatible.
pandas-gbq 0.13.3 requires google-cloud-bigquery[bqstorage,pandas]<2.0.0dev,>=1.11.1, but you have google-cloud-bigquery 2.32.0 which is incompatible.
google-colab 1.0.0 requires six~=1.15.0, but you have six 1.16.0 which is incompatible.
datascience 0.10.6 requires folium==0.2.1, but you have folium 0.8.3 which is incompatible.
albumentations 0.1.12 requires imgaug<0.2.7,>=0.2.5, but you have imgaug 0.2.9 which is incompatible.[0m
!git clone --depth 1 -b v2.3.0 https://github.com/tensorflow/models.git
fatal: destination path 'models' already exists and is not an empty directory.
# install requirements to use tensorflow/models repository
!pip install -Uqr models/official/requirements.txt
# you may have to restart the runtime afterwards
[31mERROR: pip's dependency resolver does not currently take into account all the packages that are installed. This behaviour is the source of the following dependency conflicts.
tensorflow 2.3.0 requires numpy<1.19.0,>=1.16.0, but you have numpy 1.21.5 which is incompatible.
tensorflow 2.3.0 requires scipy==1.4.1, but you have scipy 1.7.3 which is incompatible.
pandas-gbq 0.13.3 requires google-cloud-bigquery[bqstorage,pandas]<2.0.0dev,>=1.11.1, but you have google-cloud-bigquery 2.32.0 which is incompatible.
google-colab 1.0.0 requires six~=1.15.0, but you have six 1.16.0 which is incompatible.
datascience 0.10.6 requires folium==0.2.1, but you have folium 0.8.3 which is incompatible.
albumentations 0.1.12 requires imgaug<0.2.7,>=0.2.5, but you have imgaug 0.2.9 which is incompatible.[0m
Restart the Runtime
Note After installing the required Python packages, you’ll need to restart the Colab Runtime Engine (Menu > Runtime > Restart runtime…)
Task 3: Download and Import the Quora Insincere Questions Dataset
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow_hub as hub
import sys
sys.path.append('models')
from official.nlp.data import classifier_data_lib
from official.nlp.bert import tokenization
from official.nlp import optimization
/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/tensorflow_addons/utils/ensure_tf_install.py:67: UserWarning: Tensorflow Addons supports using Python ops for all Tensorflow versions above or equal to 2.6.0 and strictly below 2.9.0 (nightly versions are not supported).
The versions of TensorFlow you are currently using is 2.3.0 and is not supported.
Some things might work, some things might not.
If you were to encounter a bug, do not file an issue.
If you want to make sure you're using a tested and supported configuration, either change the TensorFlow version or the TensorFlow Addons's version.
You can find the compatibility matrix in TensorFlow Addon's readme:
https://github.com/tensorflow/addons
UserWarning,
print("TF Version: ", tf.__version__)
print("Eager mode: ", tf.executing_eagerly())
print("Hub version: ", hub.__version__)
print("GPU is", "available" if tf.config.experimental.list_physical_devices("GPU") else "NOT AVAILABLE")
TF Version: 2.3.0
Eager mode: True
Hub version: 0.12.0
GPU is available
A downloadable copy of the Quora Insincere Questions Classification data can be found https://archive.org/download/fine-tune-bert-tensorflow-train.csv/train.csv.zip. Decompress and read the data into a pandas DataFrame.
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
df = pd.read_csv(
'https://archive.org/download/fine-tune-bert-tensorflow-train.csv/train.csv.zip',
compression = 'zip', low_memory = False)
df.shape
(1306122, 3)
df.tail(20)
.dataframe tbody tr th {
vertical-align: top;
}
.dataframe thead th {
text-align: right;
}
| qid | question_text | target | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1306102 | ffff3778790af9baae76 | What steps can I take to live a normal life if... | 0 |
| 1306103 | ffff3f0a2449ffe4b9ff | Isn't Trump right after all? Why should the US... | 1 |
| 1306104 | ffff41393389d4206066 | Is 33 too late for a career in creative advert... | 0 |
| 1306105 | ffff42493fc203cd9532 | What is difference between the filteration wor... | 0 |
| 1306106 | ffff48dd47bee89fff79 | If the universe "popped" into existence from n... | 0 |
| 1306107 | ffff5fd051a032f32a39 | How does a shared service technology team meas... | 0 |
| 1306108 | ffff6d528040d3888b93 | How is DSATM civil engineering? | 0 |
| 1306109 | ffff8776cd30cdc8d7f8 | Do you know any problem that depends solely on... | 0 |
| 1306110 | ffff94d427ade3716cd1 | What are some comic ideas for you Tube videos ... | 0 |
| 1306111 | ffffa382c58368071dc9 | If you had $10 million of Bitcoin, could you s... | 0 |
| 1306112 | ffffa5b0fa76431c063f | Are you ashamed of being an Indian? | 1 |
| 1306113 | ffffae5dbda3dc9e9771 | What are the methods to determine fossil ages ... | 0 |
| 1306114 | ffffba7c4888798571c1 | What is your story today? | 0 |
| 1306115 | ffffc0c7158658a06fd9 | How do I consume 150 gms protein daily both ve... | 0 |
| 1306116 | ffffc404da586ac5a08f | What are the good career options for a msc che... | 0 |
| 1306117 | ffffcc4e2331aaf1e41e | What other technical skills do you need as a c... | 0 |
| 1306118 | ffffd431801e5a2f4861 | Does MS in ECE have good job prospects in USA ... | 0 |
| 1306119 | ffffd48fb36b63db010c | Is foam insulation toxic? | 0 |
| 1306120 | ffffec519fa37cf60c78 | How can one start a research project based on ... | 0 |
| 1306121 | ffffed09fedb5088744a | Who wins in a battle between a Wolverine and a... | 0 |
<script>
const buttonEl =
document.querySelector('#df-4fddcebe-2366-4d00-a0a9-b272beb23f67 button.colab-df-convert');
buttonEl.style.display =
google.colab.kernel.accessAllowed ? 'block' : 'none';
async function convertToInteractive(key) {
const element = document.querySelector('#df-4fddcebe-2366-4d00-a0a9-b272beb23f67');
const dataTable =
await google.colab.kernel.invokeFunction('convertToInteractive',
[key], {});
if (!dataTable) return;
const docLinkHtml = 'Like what you see? Visit the ' +
'<a target="_blank" href=https://colab.research.google.com/notebooks/data_table.ipynb>data table notebook</a>'
+ ' to learn more about interactive tables.';
element.innerHTML = '';
dataTable['output_type'] = 'display_data';
await google.colab.output.renderOutput(dataTable, element);
const docLink = document.createElement('div');
docLink.innerHTML = docLinkHtml;
element.appendChild(docLink);
}
</script>
</div>
df.target.plot(kind = 'hist', title = 'Target distribution')
<AxesSubplot:title={'center':'Target distribution'}, ylabel='Frequency'>

Task 4: Create tf.data.Datasets for Training and Evaluation
train_df, remaining = train_test_split(df, random_state = 42, train_size = 0.0075, stratify = df.target.values)
valid_df, _ = train_test_split(remaining, random_state = 42, train_size = 0.00075, stratify = remaining.target.values)
train_df.shape, valid_df.shape
((9795, 3), (972, 3))
with tf.device('/cpu:0'):
train_data = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(
(train_df['question_text'].values, train_df['target'].values)
)
valid_data = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(
(valid_df['question_text'].values, valid_df['target'].values)
)
for text, label in train_data.take(1):
print(text, label)
tf.Tensor(b'Why are unhealthy relationships so desirable?', shape=(), dtype=string) tf.Tensor(0, shape=(), dtype=int64)
Task 5: Download a Pre-trained BERT Model from TensorFlow Hub
"""
Each line of the dataset is composed of the review text and its label
- Data preprocessing consists of transforming text to BERT input features:
input_word_ids, input_mask, segment_ids
- In the process, tokenizing the text is done with the provided BERT model tokenizer
"""
# Label categories
label_list = [0, 1]
# maximum length of (token) input sequences
max_seq_length = 128
train_batch_size = 32
# Get BERT layer and tokenizer:
# More details here: https://tfhub.dev/tensorflow/bert_en_uncased_L-12_H-768_A-12/2
bert_layer = hub.KerasLayer('https://tfhub.dev/tensorflow/bert_en_uncased_L-12_H-768_A-12/2', trainable = True)
vocab_file = bert_layer.resolved_object.vocab_file.asset_path.numpy()
do_lower_case = bert_layer.resolved_object.do_lower_case.numpy()
tokenizer = tokenization.FullTokenizer(vocab_file, do_lower_case)
tokenizer.wordpiece_tokenizer.tokenize('hi, how are you doing?')
['hi', '##,', 'how', 'are', 'you', 'doing', '##?']
tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(tokenizer.wordpiece_tokenizer.tokenize('hi, how are you doing?'))
[7632, 29623, 2129, 2024, 2017, 2725, 29632]
Task 6: Tokenize and Preprocess Text for BERT
Figure 2: BERT Tokenizer
We’ll need to transform our data into a format BERT understands. This involves two steps. First, we create InputExamples using classifier_data_lib’s constructor InputExample provided in the BERT library.
# This provides a function to convert row to input features and label
def to_feature(text, label, label_list=label_list, max_seq_length=max_seq_length, tokenizer=tokenizer):
example = classifier_data_lib.InputExample(
guid = None,
text_a = text.numpy(),
text_b = None,
label = label.numpy()
)
feature = classifier_data_lib.convert_single_example(0, example, label_list, max_seq_length, tokenizer)
return (feature.input_ids, feature.input_mask, feature.segment_ids, feature.label_id)
You want to use Dataset.map to apply this function to each element of the dataset. Dataset.map runs in graph mode.
- Graph tensors do not have a value.
- In graph mode you can only use TensorFlow Ops and functions.
So you can’t .map this function directly: You need to wrap it in a tf.py_function. The tf.py_function will pass regular tensors (with a value and a .numpy() method to access it), to the wrapped python function.
Task 7: Wrap a Python Function into a TensorFlow op for Eager Execution
def to_feature_map(text, label):
input_ids, input_mask, segment_ids, label_id = tf.py_function(to_feature, inp = [text, label],
Tout = [tf.int32, tf.int32, tf.int32, tf.int32]
)
input_ids.set_shape([max_seq_length])
input_mask.set_shape([max_seq_length])
segment_ids.set_shape([max_seq_length])
label_id.set_shape([])
x = {
'input_word_ids' : input_ids,
'input_mask' : input_mask,
'input_type_ids' : segment_ids
}
return (x, label_id)
Task 8: Create a TensorFlow Input Pipeline with tf.data
with tf.device('/cpu:0'):
# train
train_data = (train_data.map(
to_feature_map,
num_parallel_calls = tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE)
.shuffle(1000)
.batch(32, drop_remainder = True)
.prefetch(tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE))
# valid
valid_data = (valid_data.map(
to_feature_map,
num_parallel_calls = tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE)
.batch(32, drop_remainder = True)
.prefetch(tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE))
The resulting tf.data.Datasets return (features, labels) pairs, as expected by keras.Model.fit:
# train data spec
train_data.element_spec
({'input_mask': TensorSpec(shape=(32, 128), dtype=tf.int32, name=None),
'input_type_ids': TensorSpec(shape=(32, 128), dtype=tf.int32, name=None),
'input_word_ids': TensorSpec(shape=(32, 128), dtype=tf.int32, name=None)},
TensorSpec(shape=(32,), dtype=tf.int32, name=None))
# valid data spec
valid_data.element_spec
({'input_mask': TensorSpec(shape=(32, 128), dtype=tf.int32, name=None),
'input_type_ids': TensorSpec(shape=(32, 128), dtype=tf.int32, name=None),
'input_word_ids': TensorSpec(shape=(32, 128), dtype=tf.int32, name=None)},
TensorSpec(shape=(32,), dtype=tf.int32, name=None))
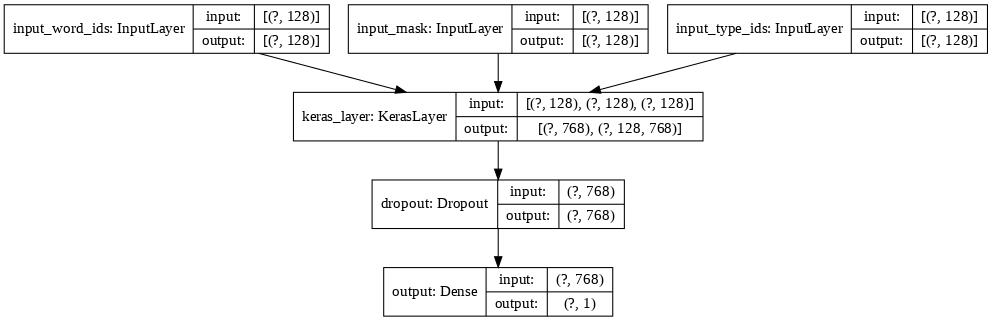
Task 9: Add a Classification Head to the BERT Layer
Figure 3: BERT Layer
# Building the model
def create_model():
input_word_ids = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=(max_seq_length,), dtype=tf.int32,
name="input_word_ids")
input_mask = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=(max_seq_length,), dtype=tf.int32,
name="input_mask")
input_type_ids = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=(max_seq_length,), dtype=tf.int32,
name="input_type_ids")
pooled_output, sequence_output = bert_layer([input_word_ids, input_mask, input_type_ids])
drop = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.4)(pooled_output)
output = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1, activation = 'sigmoid', name = 'output')(drop)
model = tf.keras.Model(
inputs = {
'input_word_ids' : input_word_ids,
'input_mask' : input_mask,
'input_type_ids' : input_type_ids
},
outputs = output
)
return model
Task 10: Fine-Tune BERT for Text Classification
model = create_model()
model.compile(
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate = 2e-5),
loss = tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(), # Using Sparse if have more than 2 classes.
metrics = [tf.keras.metrics.BinaryAccuracy()])
model.summary()
Model: "functional_1"
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param # Connected to
==================================================================================================
input_word_ids (InputLayer) [(None, 128)] 0
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
input_mask (InputLayer) [(None, 128)] 0
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
input_type_ids (InputLayer) [(None, 128)] 0
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
keras_layer (KerasLayer) [(None, 768), (None, 109482241 input_word_ids[0][0]
input_mask[0][0]
input_type_ids[0][0]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
dropout (Dropout) (None, 768) 0 keras_layer[0][0]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
output (Dense) (None, 1) 769 dropout[0][0]
==================================================================================================
Total params: 109,483,010
Trainable params: 109,483,009
Non-trainable params: 1
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(model = model, show_shapes = True, dpi = 76)
# Train model
epochs = 4
history = model.fit(train_data,
validation_data = valid_data,
epochs = epochs,
verbose = 1)
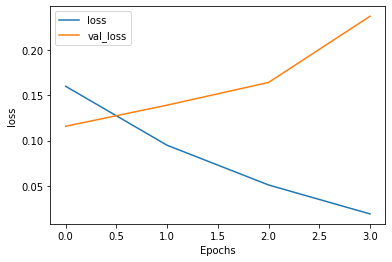
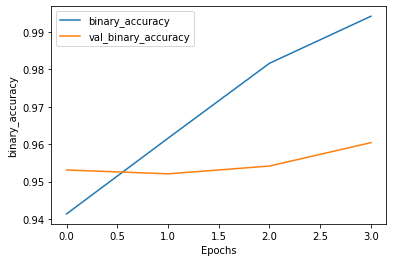
Epoch 1/4
306/306 [==============================] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1601 - binary_accuracy: 0.9414WARNING:tensorflow:Callbacks method `on_test_batch_end` is slow compared to the batch time (batch time: 0.0286s vs `on_test_batch_end` time: 0.5093s). Check your callbacks.
WARNING:tensorflow:Callbacks method `on_test_batch_end` is slow compared to the batch time (batch time: 0.0286s vs `on_test_batch_end` time: 0.5093s). Check your callbacks.
306/306 [==============================] - 484s 2s/step - loss: 0.1601 - binary_accuracy: 0.9414 - val_loss: 0.1159 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.9531
Epoch 2/4
306/306 [==============================] - 483s 2s/step - loss: 0.0949 - binary_accuracy: 0.9616 - val_loss: 0.1393 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.9521
Epoch 3/4
306/306 [==============================] - 483s 2s/step - loss: 0.0509 - binary_accuracy: 0.9816 - val_loss: 0.1644 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.9542
Epoch 4/4
306/306 [==============================] - 483s 2s/step - loss: 0.0189 - binary_accuracy: 0.9942 - val_loss: 0.2376 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.9604
Task 11: Evaluate the BERT Text Classification Model
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def plot_graphs(history, metric):
plt.plot(history.history[metric])
plt.plot(history.history['val_'+metric], '')
plt.xlabel("Epochs")
plt.ylabel(metric)
plt.legend([metric, 'val_'+metric])
plt.show()
plot_graphs(history, 'loss')
plot_graphs(history, 'binary_accuracy')
sample_example = ['hello, have a good day', 'are you feeling ashame being an asian?']
test_data = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((sample_example, [0] * len(sample_example)))
test_data = (test_data.map(to_feature_map).batch(1))
preds = model.predict(test_data)
threshold = 0.5 # between 0 and 1
['Insincere' if pred >= threshold else 'Sincere' for pred in preds]
['Sincere', 'Sincere']